bios系统英文,Understanding BIOS: The Basics
时间:2024-11-23 来源:网络 人气:
Understanding BIOS: The Basics
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is a crucial component of your computer that initializes hardware components and provides the necessary instructions for the operating system to load. This article delves into the basics of BIOS, its functions, and why it is essential for the smooth operation of your computer.
What is BIOS?
BIOS is a firmware that is stored on a chip on the motherboard of your computer. It is responsible for performing a Power-On Self-Test (POST) when you turn on your computer. The POST checks the hardware components to ensure they are functioning correctly before the operating system takes over.
Functions of BIOS
Here are some of the primary functions of BIOS:
Power-On Self-Test (POST): This checks the hardware components, such as the CPU, memory, and storage devices, to ensure they are working correctly.
Boot Sequence: BIOS determines the order in which the computer searches for the operating system to load. This can be set to boot from the hard drive, CD/DVD, USB, or network.
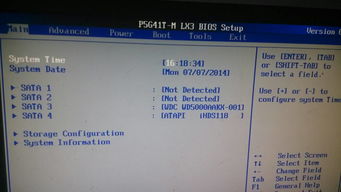
CMOS Setup: This is where you can configure various settings, such as the date and time, boot order, and hardware settings.
BIOS Update: Updating the BIOS can fix bugs, improve performance, and add support for new hardware.
Accessing BIOS
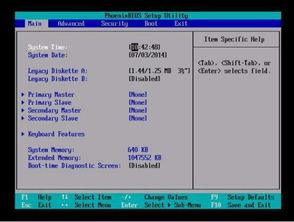
Accessing the BIOS setup menu is essential for configuring your computer's hardware and boot options. Here's how to access the BIOS on different types of computers:
Desktop Computers: Typically, you can enter the BIOS by pressing a key during the boot process, such as F2, Del, or Esc. The specific key may vary depending on the manufacturer.
Laptops: Similar to desktops, laptops also require pressing a key during boot. Common keys include F2, F10, or Del. Check your laptop's manual for the exact key.
Netbooks and Tablets: These devices may not have a BIOS setup menu, as they often use a different firmware called UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface).
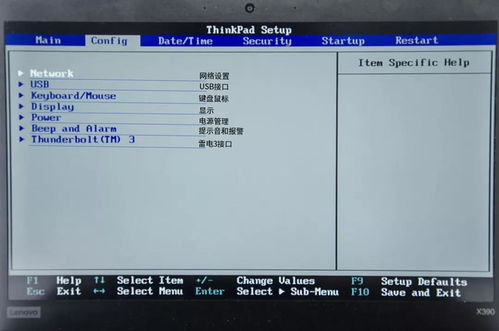
BIOS Setup Menu
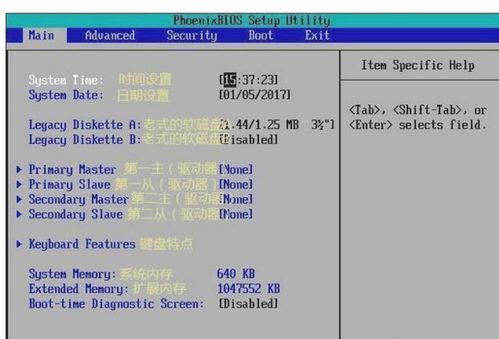
Once you have entered the BIOS setup menu, you will see several tabs and options. Here are some common sections you might encounter:
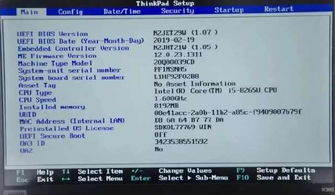
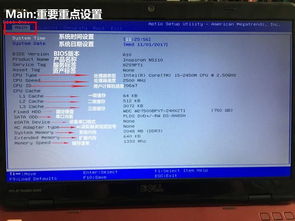
Main: This tab displays basic system information, such as the BIOS version, CPU type, and memory size.
Advanced: This section allows you to configure advanced hardware settings, such as CPU clock speeds, memory timings, and power management options.
Security: Here, you can set passwords to prevent unauthorized access to your computer and the BIOS setup menu.
Boot: This tab allows you to configure the boot order and other boot-related settings, such as enabling or disabling the boot from USB option.
Exit: Use this tab to save your changes and exit the BIOS setup menu.
BIOS vs. UEFI
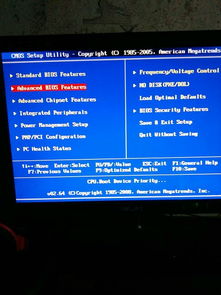
While BIOS has been the standard firmware for decades, UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a newer and more advanced firmware standard. UEFI offers faster boot times, better security features, and support for larger hard drives and more memory. Most modern computers use UEFI instead of BIOS.
Conclusion
BIOS is a critical component of your computer that ensures hardware components work correctly and the operating system loads. Understanding the basics of BIOS and how to access and navigate the BIOS setup menu can help you configure your computer's hardware and boot options. Whether you're updating the BIOS, changing the boot order, or setting passwords, knowing how to work with BIOS is an essential skill for any computer user.
Tags:
BIOS, firmware, computer, hardware, operating system, boot, setup, configuration, UEFI
相关推荐
教程资讯
教程资讯排行
- 1 系统声音小,电脑声音调到100还是太小了怎么调
- 2 联想r400硬件升级教程,联想ThinkPad R400硬件升级教程
- 3 4s流畅系统版本,哪个版本最值得选择?
- 4 32位的cpu能装64位的系统吗,32位CPU能否安装64位系统?全面解析
- 5 e450系统还原,联想ThinkPad E450系统还原指南
- 6 错误模块ntedll微信,原因及解决方法详解
- 7 4s 613系统,2024苹果4s降级613自制固件下载
- 8 显示系统工程,技术发展与应用前景
- 9 alienware系统u盘重装,Alienware笔记本系统U盘重装全攻略
- 10 联想硬盘保护系统升级,轻松实现系统优化与功能扩展