
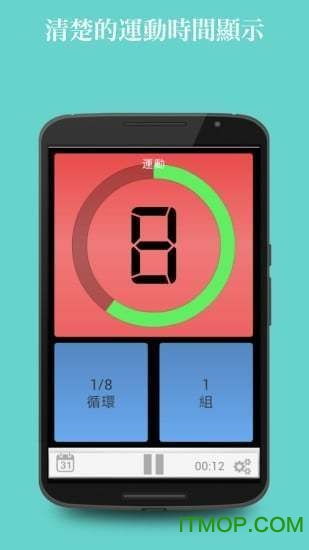
悬浮秒表安卓版

- 文件大小:16.54MB
- 界面语言:简体中文
- 文件类型:Android
- 授权方式:5G系统之家
- 软件类型:装机软件
- 发布时间:2024-10-24
- 运行环境:5G系统之家
- 下载次数:268
- 软件等级:
- 安全检测: 360安全卫士 360杀毒 电脑管家
系统简介
前端高效计时器工具实现与优化指南

在当今的前端开发领域,计时器工具的应用日益广泛。无论是实现倒计时、定时任务,还是进行间隔刷新,计时器都是不可或缺的功能。本文将深入探讨如何实现一个高效的前端计时器工具,并对其优化和应用方法进行详细解析。
计时器基本概念

首先,我们需要了解计时器的基本概念。在JavaScript中,`setTimeout`和`setInterval`是两个常用的计时器函数。`setTimeout`用于执行一次性延迟任务,而`setInterval`则用于周期性任务。
- `setTimeout`:该函数接受两个参数,第一个是执行函数,第二个是延迟时间(毫秒)。例如,`setTimeout(function() { console.log('Hello, world!'); }, 1000);`将在1秒后执行打印“Hello, world!”的操作。
- `setInterval`:与`setTimeout`类似,但`setInterval`会重复执行指定的函数,直到调用`clearInterval`函数停止。例如,`setInterval(function() { console.log('Tick...'); }, 1000);`将每秒执行一次打印“Tick...”的操作。
计时器类实现

为了实现一个具有开始、暂停、继续和重置功能的计时器,我们可以创建一个计时器类。以下是一个简单的计时器类实现示例:
```javascript
class Timer {
constructor(duration) {
this.duration = duration;
this.startTime = null;
this.remaining = duration;
this.timerId = null;
start() {
this.startTime = Date.now();
this.timerId = setInterval(() => {
this.remaining = this.duration - Math.floor((Date.now() - this.startTime) / 1000);
console.log(`Remaining time: ${this.remaining} seconds`);
if (this.remaining <= 0) {
this.stop();
}
}, 1000);
pause() {
if (this.timerId) {
clearInterval(this.timerId);
this.timerId = null;
}
resume() {
if (!this.timerId) {
this.startTime = Date.now() - this.remaining 1000;
this.start();
}
reset() {
this.remaining = this.duration;
if (this.timerId) {
this.pause();
}
stop() {
if (this.timerId) {
clearInterval(this.timerId);
this.timerId = null;
}
console.log('Timer stopped.');
避免回调地狱

在使用计时器类时,我们应避免回调地狱,推荐使用`Promise`或`async/await`来处理异步任务。以下是一个使用`async/await`的示例:
```javascript
async function runTimer() {
const timer = new Timer(10);
await timer.start();
await timer.pause();
await timer.resume();
await timer.reset();
await timer.stop();
资源管理和内存泄漏

在实现计时器工具时,资源管理和避免内存泄漏至关重要。确保在不再需要计时器时,及时调用`stop`方法来清除定时器,避免内存泄漏。
实际应用场景

- 倒计时功能:在电商网站中,倒计时可以用来显示商品促销活动的剩余时间。
- 动态页面刷新:在新闻网站中,可以使用计时器来实现定时刷新页面内容。

- 前端动画:在动画制作中,可以使用计时器来控制动画的播放速度。
本文介绍了如何实现一个高效的前端计时器工具,并对其优化和应用方法进行了详细解析。通过合理使用`setTimeout`、`setInterval`以及`Promise`或`async/await`,我们可以创建出功能强大且易于维护的计时器工具。在实际应用中,计时器工具可以帮助我们实现各种时间相关的功能,提升用户体验。
常见问题
- 2025-11-10 哈啰出行
- 2025-11-10 微粉猫微商软件最新版下载2024
- 2025-11-10 你是什么梗
- 2025-11-10 众恩金融
装机软件下载排行

其他人正在下载
- 芒物元宇宙商城
- 时尚芭莎手机版
- nice数藏app
- 日淘酱代购安卓版
- 美多萌最新版
- 生动科学免费版
- tokenpocket最新v1.8.7版下载
- 小狐狸官网钱包最新版
- Letstalk官方正版
- whatsapp官方最新版下载






