供配电系统外文翻译,An Overview of Power Supply and Distribution Systems
时间:2024-12-23 来源:网络 人气:
An Overview of Power Supply and Distribution Systems

With the rapid development of modern society, the demand for electricity has been increasing significantly. Power supply and distribution systems play a crucial role in ensuring the stable and reliable supply of electricity to various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial applications. This article provides an overview of power supply and distribution systems, highlighting their components, functions, and challenges.
Components of Power Supply and Distribution Systems
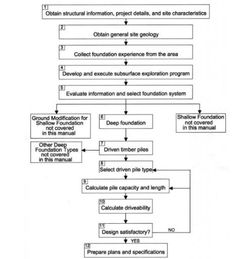
Power supply and distribution systems consist of several key components that work together to deliver electricity from the generation source to the end-users. The main components include:
1. Generation Station
The generation station is where electricity is produced. It can be powered by various sources, such as fossil fuels, nuclear energy, hydroelectric power, wind, solar, and geothermal energy. The generated electricity is typically at a high voltage to facilitate efficient transmission over long distances.
2. Transmission Lines
Transmission lines are high-voltage electrical conductors that carry electricity from the generation station to the distribution network. These lines are designed to minimize energy loss during transmission and ensure the stable flow of electricity. They are often constructed using overhead towers or underground cables, depending on the specific requirements and environmental considerations.
3. Substations

Substations are critical facilities that facilitate the transformation of high-voltage electricity from the transmission lines to lower voltages suitable for distribution. They also provide protection, control, and monitoring functions to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the power system. Substations are equipped with transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment necessary for voltage regulation and protection.
4. Distribution Network
The distribution network is responsible for delivering electricity from the substation to the end-users. It consists of a series of transformers, distribution lines, and distribution transformers that step down the voltage to a level suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial use. The distribution network is designed to be flexible and reliable, allowing for the connection of various types of loads.
Functions of Power Supply and Distribution Systems

Power supply and distribution systems perform several essential functions to ensure the reliable supply of electricity:
1. Reliability
Reliability is a critical aspect of power supply and distribution systems. It involves minimizing downtime and ensuring that electricity is available when and where it is needed. This is achieved through redundancy, maintenance, and continuous monitoring of the system.
2. Efficiency
Efficiency refers to the ability of the power system to deliver electricity with minimal energy loss. This is achieved through the use of advanced technologies, such as high-efficiency transformers, smart grids, and energy management systems. Efficient power systems reduce costs and environmental impact.
3. Safety
Safety is paramount in power supply and distribution systems. It involves protecting personnel, equipment, and the environment from potential hazards. This is achieved through the implementation of safety standards, regular maintenance, and emergency response procedures.
Challenges in Power Supply and Distribution Systems
Despite the advancements in technology and infrastructure, power supply and distribution systems face several challenges:
1. Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The increasing demand for clean energy has led to the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the power supply mix. This integration presents challenges related to voltage regulation, frequency control, and grid stability.
2. Smart Grids

Smart grids are advanced power systems that use digital technology to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity delivery. The development and implementation of smart grids require significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
3. Urbanization

Urbanization has led to an increased demand for electricity in densely populated areas. This has resulted in the need for more efficient and reliable power supply and distribution systems to meet the growing energy needs of urban populations.
教程资讯
教程资讯排行