给排水系统的英语,Introduction to Drainage and Sewage Systems
时间:2024-11-28 来源:网络 人气:
Introduction to Drainage and Sewage Systems
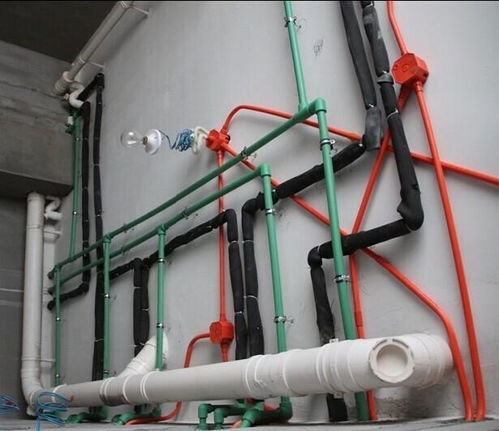

Drainage and sewage systems are essential components of urban infrastructure, ensuring the efficient removal and treatment of waste water and rainwater. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining public health, preventing environmental pollution, and preserving the aesthetic appeal of urban landscapes. In this article, we will explore the basics of drainage and sewage systems, their components, and their significance in modern society.
Components of Drainage Systems

Drainage systems are designed to collect and transport rainwater and surface runoff away from urban areas. The primary components of a drainage system include:
Drainage Channels: These are the main pathways through which water flows. They can be made of concrete, asphalt, or other materials and are designed to handle large volumes of water.
Storm Drains: These are specifically designed to collect and channel stormwater from streets, parking lots, and other surfaces. Storm drains are often equipped with grates to prevent debris from entering the system.
Subsurface Drains: These are installed beneath the ground to collect water from the soil and redirect it to the main drainage channels.
Drainage Pumps: In areas with high water tables or where gravity drainage is not sufficient, drainage pumps are used to move water to the main drainage channels.
Components of Sewage Systems
Sewage systems are responsible for the collection, transport, and treatment of wastewater from residential, commercial, and industrial sources. The key components of a sewage system include:
Sewer Pipes: These are the main conduits that carry wastewater from buildings and streets to treatment plants. Sewer pipes are typically made of materials such as vitrified clay, concrete, or plastic.
Sewage Pump Stations: In areas where the natural slope of the terrain is insufficient for gravity flow, sewage pump stations are used to lift wastewater to higher elevations.
Sewage Treatment Plants: These facilities treat wastewater to remove pollutants and make it safe for discharge into water bodies or for reuse. Treatment processes may include physical, chemical, and biological methods.
Overflow Structures: These structures are designed to prevent the overflow of untreated wastewater during heavy rainfall or periods of high demand.
Significance of Drainage and Sewage Systems
The proper functioning of drainage and sewage systems is vital for several reasons:
Public Health: Effective drainage and sewage systems prevent the spread of diseases caused by contaminated water and waste.
Environmental Protection: By treating wastewater, these systems help protect water bodies from pollution and maintain ecological balance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Properly managed drainage and sewage systems contribute to the overall cleanliness and beauty of urban environments.
Resource Conservation: By treating wastewater, these systems can recover valuable resources such as nutrients and water, which can be reused for irrigation or industrial processes.
Challenges and Innovations in Drainage and Sewage Systems
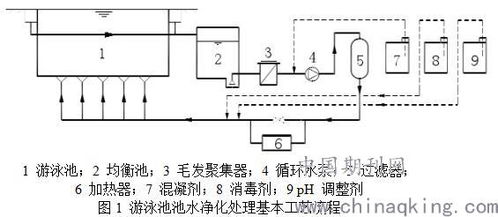
Despite the importance of drainage and sewage systems, there are several challenges associated with their design, construction, and maintenance:
Urban Growth: As cities expand, the demand for efficient drainage and sewage systems increases, often requiring upgrades and extensions to existing infrastructure.
Climate Change: The impact of climate change, including more frequent and severe storms, poses new challenges for drainage systems, requiring them to be more resilient and adaptable.
Old Infrastructure: Many urban areas have outdated drainage and sewage systems that are in need of repair or replacement.
In response to these challenges, innovative solutions are being developed, such as:
Green Infrastructure: Incorporating natural elements like green roofs, rain gardens, and permeable pavements to manage stormwater at the source.
Smart Technology: Utilizing sensors, data analytics, and automated controls to optimize
相关推荐
教程资讯
教程资讯排行